Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; Ibaraki University*
JAEA-Review 2023-021, 112 Pages, 2024/02
The Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2020. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in the nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. (TEPCO). For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2018, this report summarizes the research results of the "Contribution to Risk Reduction in Decommissioning Works by the Elucidation of Basic Property of Radioactive Microparticles" conducted from FY2018 to FY2021 (this contract was extended to FY2021). The present study aims to understand the basic properties (size, chemical composition, isotopic composition - including concentration of  -emitters, electrostatic properties, and optical properties, etc.) of fine particles composed of silicate with insoluble properties which contain regions of highly concentrated radioactive cesium (Cs) released to the environment by the accident at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station of TEPCO in 2011 March.
-emitters, electrostatic properties, and optical properties, etc.) of fine particles composed of silicate with insoluble properties which contain regions of highly concentrated radioactive cesium (Cs) released to the environment by the accident at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station of TEPCO in 2011 March.
Miyagawa, Akihisa*; Hayashi, Naoki*; Kuzure, Yoshiaki*; Takahashi, Takumi*; Iwamoto, Hibiki*; Arai, Tsuyoshi*; Nagatomo, Shigenori*; Miyazaki, Yasunori; Hasegawa, Kenta; Sano, Yuichi; et al.
Bulletin of the Chemical Society of Japan, 96(7), p.671 - 676, 2023/07
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:71.3(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)We investigated the distribution mechanism of Eu(III) in a single polymer-coated silica particle including nitrilotriacetamide (NTA) extractants known as HONTA and TOD2EHNTA. The present study provides a valuable approach for the evaluation and enhancement of the functionality of "single extractant-impregnated polymer-coated silica particle".
 synchrotron X-ray scattering and nanoindentation test
synchrotron X-ray scattering and nanoindentation testIm, S.*; Jee, H.*; Suh, H.*; Kanematsu, Manabu*; Morooka, Satoshi; Choe, H.*; Nishio, Yuhei*; Machida, Akihiko*; Kim, J.*; Lim, S.*; et al.
Construction and Building Materials, 365, p.130034_1 - 130034_18, 2023/02
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:70.19(Construction & Building Technology)Miyakawa, Kazuya; Kashiwaya, Koki*; Komura, Yuto*; Nakata, Kotaro*
Geochemical Journal, 57(5), p.155 - 175, 2023/00
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Geochemistry & Geophysics)In the thick marine sediments, groundwater altered from seawater during the burial diagenesis may exist. Such altered ancient seawater will be called fossil seawater. In such a field, groundwater flow is considered extremely slow because it is not affected by the seepage of meteoric water even after the uplift. During diagenesis, dehydration from silicates causes changes such as a decrease in the salinity of the porewater. However, dehydration reactions alone cannot quantitatively explain water chemistry changes. In this study, we developed an analytical model that considers the dehydration reaction from silicates during the burial process and the upward migration of porewater due to compaction and examined the possible evolution of porewater chemistry. The results showed that the water chemistry, which was strongly influenced by the dehydration reaction from opal-A to quartz and from smectite, was similar to the observations from boring surveys. The results suggest that the fossil seawater formed during the diagenesis may have been preserved since the uplift and strongly supports the slow groundwater flow in the area where the fossil seawater exists.
Kim, G.*; Im, S.*; Jee, H.*; Suh, H.*; Cho, S.*; Kanematsu, Manabu*; Morooka, Satoshi; Koyama, Taku*; Nishio, Yuhei*; Machida, Akihiko*; et al.
Cement and Concrete Research, 159, p.106869_1 - 106869_17, 2022/09
Times Cited Count:18 Percentile:87.96(Construction & Building Technology) and GeO
and GeO liquids
liquidsKawaguchi, Munemichi; Uno, Masayoshi*
Journal of Crystal Growth, 585, p.126590_1 - 126590_7, 2022/05
Phase-field mobility,  , and crystal growth rates in crystallization of 11 oxides or mixed oxides in undercooled silicates, SiO
, and crystal growth rates in crystallization of 11 oxides or mixed oxides in undercooled silicates, SiO and GeO
and GeO liquids were calculated with a simple phase-field model (PFM), and material dependence of the
liquids were calculated with a simple phase-field model (PFM), and material dependence of the  was discussed. Ratios between experimental crystal growth rates and the PFM simulation with
was discussed. Ratios between experimental crystal growth rates and the PFM simulation with 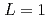 were confirmed to be proportional to a power of
were confirmed to be proportional to a power of 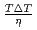 on the solid/liquid interface process during the crystal growth in a log-log plot. We determined that parameters,
on the solid/liquid interface process during the crystal growth in a log-log plot. We determined that parameters,  and
and  , of the
, of the 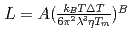 were
were 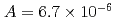 to
to 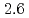 m
m J
J s
s and
and 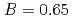 to
to 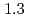 , which were unique for the materials. It was confirmed that our PFM simulation with the determined
, which were unique for the materials. It was confirmed that our PFM simulation with the determined  reproduced quantitively the experimental crystal growth rates. The
reproduced quantitively the experimental crystal growth rates. The  has a proportional relationship with the diffusion coefficient of a cation molar mass average per unit an oxygen molar mass at
has a proportional relationship with the diffusion coefficient of a cation molar mass average per unit an oxygen molar mass at 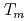 in a log-log graph. The
in a log-log graph. The  depends on the sum of the cation molar mass per the oxygen molar mass,
depends on the sum of the cation molar mass per the oxygen molar mass, 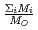 , in a compound. In
, in a compound. In 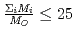 , the
, the  decreases with the cation molar mass increasing. The assumed cause is that the B represents the degree of the temperature dependence of the
decreases with the cation molar mass increasing. The assumed cause is that the B represents the degree of the temperature dependence of the  . Since the cation molar mass is proportional to an inertial resistance of the cation transfer, the
. Since the cation molar mass is proportional to an inertial resistance of the cation transfer, the  decreases with inverse of the cation molar mass. In crystallization of the silicates of heavy cation in
decreases with inverse of the cation molar mass. In crystallization of the silicates of heavy cation in 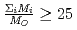 , the
, the  saturates at approximately 0.67, which leads to
saturates at approximately 0.67, which leads to 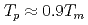 .
.
Im, S.*; Jee, H.*; Suh, H.*; Kanematsu, Manabu*; Morooka, Satoshi; Koyama, Taku*; Nishio, Yuhei*; Machida, Akihiko*; Kim, J.*; Bae, S.*
Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 104(9), p.4803 - 4818, 2021/09
Times Cited Count:18 Percentile:85.31(Materials Science, Ceramics)Myagmarjav, O.; Tanaka, Nobuyuki; Nomura, Mikihiro*; Noguchi, Hiroki; Imai, Yoshiyuki; Kamiji, Yu; Kubo, Shinji; Takegami, Hiroaki
Progress in Nuclear Energy, 137, p.103772_1 - 103772_7, 2021/07
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:72.21(Nuclear Science & Technology)Sato, Junya; Shiota, Kenji*; Takaoka, Masaki*
Zairyo, 70(5), p.406 - 411, 2021/05
An aluminosilicate solid is an inorganic material that has the property of immobilizing heavy metals or radionuclides in the matrix. In this study, aluminosilicates with a Si/Al molar ratio of 0.5 was synthesized from a chemical reagent in order to produce aluminosilicate solids with a low Si/Al molar ratio, which were expected to improve the immobilization of heavy metals and radionuclides contained in the matrix. The synthesized Si-Al gel with a Si/Al molar ratio of 0.5 had little impurity content and was in an amorphous phase. In addition, the compressive strength of the aluminosilicate solid produced by the synthesized Si-Al gel showed a 5 MPa or more, confirming that it can be used as a raw material for aluminosilicate solids. The aluminosilicate solid with a Si/Al molar ratio of 1.25 had a dense surface structure from the result of BSE images and had the highest compressive strength among all samples.
Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; Ibaraki University*
JAEA-Review 2020-033, 84 Pages, 2021/01
JAEA/CLADS had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project in FY2019. Among the adopted proposals in FY2018, this report summarizes the research results of the "Contribution to Risk Reduction in Decommissioning Works by the Elucidation of Basic Property of Radioactive Microparticles" conducted in FY2019.
 O-2SiO
O-2SiO , Na
, Na O-2SiO
O-2SiO and K
and K O-2SiO
O-2SiO
Kawaguchi, Munemichi; Uno, Masayoshi*
Journal of the Ceramic Society of Japan, 128(10), p.832 - 838, 2020/10
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:17(Materials Science, Ceramics)This study developed phase-field method (PFM) technique in oxide melt system by using a new mobility coefficient ( ). The crystal growth rates (
). The crystal growth rates (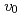 ) obtained by the PFM calculation with the constant
) obtained by the PFM calculation with the constant  were comparable to the thermodynamic driving force in normal growth model. The temperature dependence of the
were comparable to the thermodynamic driving force in normal growth model. The temperature dependence of the  was determined from the experimental crystal growth rates and the
was determined from the experimental crystal growth rates and the 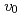 . Using the determined
. Using the determined  , the crystal growth rates (
, the crystal growth rates ( ) in alkali disilicate glasses, Li
) in alkali disilicate glasses, Li O-2SiO
O-2SiO , Na
, Na O-2SiO
O-2SiO and K
and K O-2SiO
O-2SiO were simulated. The temperature dependence of the
were simulated. The temperature dependence of the  was qualitatively and quantitatively so similar that the PFM calculation results demonstrated the validity of the
was qualitatively and quantitatively so similar that the PFM calculation results demonstrated the validity of the  . Especially, the
. Especially, the  obtained by the PFM calculation appeared the rapid increase just below the thermodynamic melting point (
obtained by the PFM calculation appeared the rapid increase just below the thermodynamic melting point (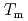 ) and the steep peak at around
) and the steep peak at around 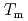 -100 K. Additionally, as the temperature decreased, the
-100 K. Additionally, as the temperature decreased, the  apparently approached zero ms
apparently approached zero ms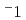 , which is limited by the
, which is limited by the  representing the interface jump process. Furthermore, we implemented the PFM calculation for the variation of the parameter
representing the interface jump process. Furthermore, we implemented the PFM calculation for the variation of the parameter  in the
in the  . As the
. As the  increased from zero to two, the peak of the
increased from zero to two, the peak of the  became steeper and the peak temperature of the
became steeper and the peak temperature of the  shifted to the high temperature side. The parameters
shifted to the high temperature side. The parameters  and
and  in the
in the  increased exponentially and decreased linearly as the atomic number of the alkali metal increased due to the ionic potential, respectively. This calculation revealed that the
increased exponentially and decreased linearly as the atomic number of the alkali metal increased due to the ionic potential, respectively. This calculation revealed that the  and
and  in the
in the  were close and reasonable for each other.
were close and reasonable for each other.
Onishi, Takashi; Koyama, Shinichi; Mimura, Hitoshi*
Nihon Ion Kokan Gakkai-Shi, 31(3), p.43 - 49, 2020/10
Rizaal, M.; Nakajima, Kunihisa; Saito, Takumi*; Osaka, Masahiko; Okamoto, Koji*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 57(9), p.1062 - 1073, 2020/09
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:71.58(Nuclear Science & Technology)The interaction of cesium hydroxide and a calcium silicate insulation material was experimentally investigated at high temperature conditions. A thermogravimetry equipped with differential thermal analysis was used to analyze thermal events in the samples of mixed calcium silicate and cesium hydroxide under Ar-5%H and Ar-4%H
and Ar-4%H -20%H
-20%H 0 with maximum temperature of 1100
0 with maximum temperature of 1100 C. Prior being mixed with cesium hydroxide, a part of calcium silicate was pretreated at high temperature to evaluate the effect of possible structural changes of this material due to a preceding thermal history and also the sake of thermodynamic evaluation to those available ones. Based upon the initial condition (preliminary heat treatment) of calcium silicate, it was found that if the original material consisted of xonotlite (Ca
C. Prior being mixed with cesium hydroxide, a part of calcium silicate was pretreated at high temperature to evaluate the effect of possible structural changes of this material due to a preceding thermal history and also the sake of thermodynamic evaluation to those available ones. Based upon the initial condition (preliminary heat treatment) of calcium silicate, it was found that if the original material consisted of xonotlite (Ca Si
Si 0
0 (0H)
(0H) ), the endothermic reaction with cesium hydroxide occurred over the temperature range 575-730
), the endothermic reaction with cesium hydroxide occurred over the temperature range 575-730 C meanwhile if the crystal phase of original material was changed to wollastonite (CaSi0
C meanwhile if the crystal phase of original material was changed to wollastonite (CaSi0 ), the interaction occurred over temperature range 700-1100
), the interaction occurred over temperature range 700-1100 C. Furthermore, the X-ray diffraction analyses have indicated on both type of pretreated calsils that regardless of Ar-5%H
C. Furthermore, the X-ray diffraction analyses have indicated on both type of pretreated calsils that regardless of Ar-5%H and Ar-4%H
and Ar-4%H -20%H
-20%H 0 atmosphere, cesium aluminum silicate, CsAlSi0
0 atmosphere, cesium aluminum silicate, CsAlSi0 was formed with aluminum in the samples as an impurity or adduct.
was formed with aluminum in the samples as an impurity or adduct.
Myagmarjav, O.; Tanaka, Nobuyuki; Nomura, Mikihiro*; Kubo, Shinji
International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 44(59), p.30832 - 30839, 2019/11
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:33.23(Chemistry, Physical)Otaka, Toshiki*; Sato, Tatsumi*; Ono, Shimpei; Nagoshi, Kohei; Abe, Ryoji*; Arai, Tsuyoshi*; Watanabe, So; Sano, Yuichi; Takeuchi, Masayuki; Nakatani, Kiyoharu*
Analytical Sciences, 35(10), p.1129 - 1133, 2019/10
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:40.49(Chemistry, Analytical)Ito, Chikara; Naito, Hiroyuki; Ishikawa, Takashi; Ito, Keisuke; Wakaida, Ikuo
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 24, p.011038_1 - 011038_6, 2019/01
A high-radiation resistant optical fiber has been developed in order to investigate the interiors of the reactor pressure vessels and the primary containment vessels at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station. The tentative dose rate in the reactor pressure vessels is assumed to be up to 1 kGy/h. We developed a radiation resistant optical fiber consisting of a 1000 ppm hydroxyl doped pure silica core and 4 % fluorine doped pure silica cladding. We attempted to apply the optical fiber to remote imaging technique by means of fiberscope. The number of core image fibers was increased from 2000 to 22000 for practical use. The transmissive rate of infrared images was not affected after irradiation of 1 MGy. No change in the spatial resolution of the view scope by means of image fiber was noted between pre- and post-irradiation. We confirmed the applicability of the probing system, which consists of a view scope using radiation-resistant optical fibers.
Yoshida, Koji*; Inoue, Takuya*; Torigoe, Motokatsu*; Yamada, Takeshi*; Shibata, Kaoru; Yamaguchi, Toshio*
Journal of Chemical Physics, 149(12), p.124502_1 - 124502_10, 2018/09
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:17.83(Chemistry, Physical)Differential scanning calorimetry, X-ray diffraction, and quasi-elastic neutron scattering (QENS) measurements of aqueous glycine solutions confined in mesoporous silica (MCM-41) were performed at different glycine concentrations, pH, and loading ratio (= mass of glycine solution / mass of dry MCM-41) in the temperature range from 305 to 180 K to discuss the confinement effect on the thermal behavior, the structure, and the dynamic properties of the solutions.
Myagmarjav, O.; Tanaka, Nobuyuki; Nomura, Mikihiro*; Kubo, Shinji
International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 42(49), p.29091 - 29100, 2017/12
Times Cited Count:20 Percentile:51.38(Chemistry, Physical)The catalytic decomposition of hydrogen iodide in a membrane reactor using silica membranes derived from hexyltrimethoxysilane (HTMOS) was investigated for the production of hydrogen in the thermochemical water splitting iodine-sulfur process. The silica membranes were prepared by counter-diffusion chemical vapor deposition using porous alumina support tubes in both the absence and presence of a  -alumina layer. The silica membranes formed on
-alumina layer. The silica membranes formed on  -alumina-coated
-alumina-coated  -alumina tubes displayed a higher H
-alumina tubes displayed a higher H permeance than that formed directly on an
permeance than that formed directly on an  -alumina tube. A silica membrane based on a 1.5
-alumina tube. A silica membrane based on a 1.5  m-thick
m-thick  -alumina layer fabricated under deposition conditions of 450
-alumina layer fabricated under deposition conditions of 450 C, 1200 s, and a N
C, 1200 s, and a N carrier gas velocity of 0.044 m s
carrier gas velocity of 0.044 m s exhibited a high H
exhibited a high H permeance of 9.4
permeance of 9.4  10
10 mol Pa
mol Pa m
m s
s while maintaining an H
while maintaining an H /N
/N selectivity of over 80.0. The performance of a membrane reactor based on an HTMOS-derived silica membrane was evaluated at 400
selectivity of over 80.0. The performance of a membrane reactor based on an HTMOS-derived silica membrane was evaluated at 400 C by measuring the HI conversion and H
C by measuring the HI conversion and H flow rates. The conversion was approximately 0.48 when the HI flow rate was 9.7 mL min
flow rates. The conversion was approximately 0.48 when the HI flow rate was 9.7 mL min .
.
 -permselective silica membrane for the separation of H
-permselective silica membrane for the separation of H from the hydrogen iodide decomposition reaction in the iodine-sulfur process
from the hydrogen iodide decomposition reaction in the iodine-sulfur processMyagmarjav, O.; Ikeda, Ayumi*; Tanaka, Nobuyuki; Kubo, Shinji; Nomura, Mikihiro*
International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 42(9), p.6012 - 6023, 2017/03
Times Cited Count:19 Percentile:49.58(Chemistry, Physical)Tsuji, Masakuni*; Kobayashi, Shinji*; Sato, Toshinori; Mikake, Shinichiro; Matsui, Hiroya
Proceedings of 8th Nordic Grouting Symposium, p.171 - 185, 2016/09
This paper presents the application of a durable liquid-type colloidal silica grout (CSG), to the great depth of the Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory (MIU). The CSG had been invented decades ago in Japan for the purpose of the ground improvement. A post-grouting experiment with the CSG carried out in 300 m depth of MIU confirmed its applicability and good durability at a great depth more than 3 years. Furthermore, a comparison study of applying the CSG between this experiment and a Swedish project indicated good applicability of the Swedish theoretical design to MIU. The CSG with the Swedish design were applied to the post-grouting campaign in a gallery at 500 m depth for further reducing water ingress and for developing the latest grouting methodology. The grouting was successful in reducing the abundant inflow from the rock with many fractures. The conductivity of the grouted rock mass of the latter fans is estimated to be lower than 10 m/s.
m/s.